Many of us hop into bed each night without ever thinking about the stages of our sleep cycle and what happens after we close our eyes.
During your sleep, you experience 4-6 cycles of REM sleep, or “rapid eye movement” sleep and your brain is very active during these periods. REM sleep makes up about 25% of your time spent asleep. This cycle is key to unlocking a wealth of health benefits!
Understanding the benefits of REM sleep is important to your overall well being. You can make healthy choices to maximize your time spent in this stage of sleep. This sleep period greatly impacts your wellbeing and affects memory, focus, and mood! While it is essential to ensure you are getting a full night’s sleep, sleep duration is only one part of the equation.
Components That Affect REM Sleep
Sleep cycles vary based on age and will shift throughout our lifetime. Infants spend about 50% of their rest time in REM sleep, while elderly people spend little time in REM sleep. Our lifestyle choices affect the function of our sleep cycle, such as alcohol consumption or other stimulants, high stress, and screen time.
Alcohol consumption decreases REM sleep early on in the night and then rebounds and prolongs REM stages when the effects wear off. This disruption is not supportive of a healthy sleep cycle. Irregular sleep patterns over an extended time can cause abnormal sleep cycles, which have many health repercussions.
REM v.s non-REM
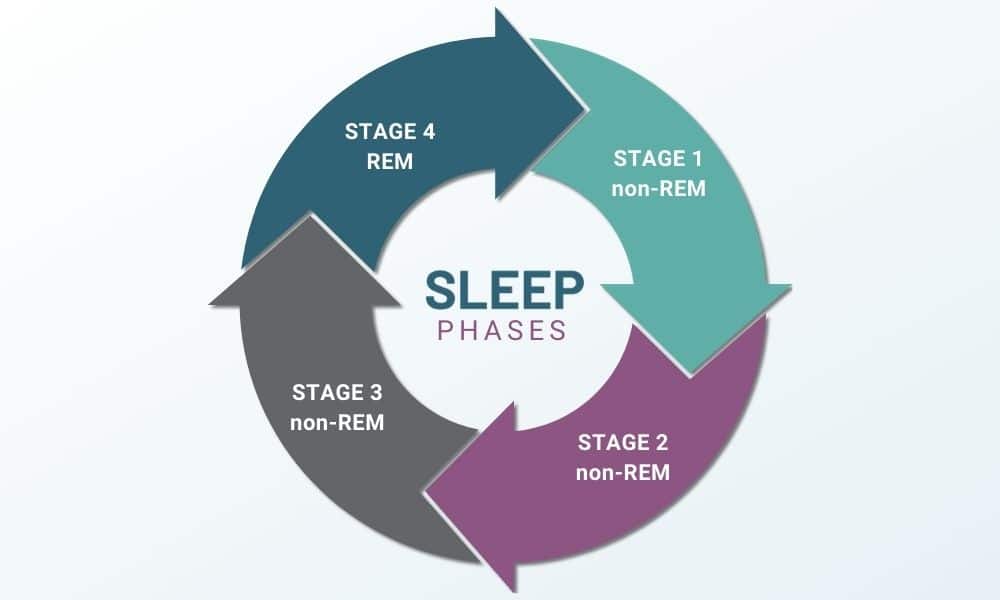
Everyone’s sleep cycle has periods of non-REM sleep and REM sleep. There are three phases of non-REM sleep, and then follows the stage of REM sleep. REM stands for “Rapid Eye Movement” and it first occurs about an hour and a half after you have fallen asleep and will happen a few times throughout the duration of sleep. Non-REM sleep is when your brain activity is decreased, and your eyes don’t move much.
There are four stages of sleep that you cycle through a few times throughout the night.
On an average night, a person goes through these stages of sleep about 4-6 times. Each sleep phase gets longer each time you cycle through it.
When you drift into sleep, you begin in non-REM sleep, broken out into three stages. After you pass through non-REM sleep phases, you will achieve REM sleep.
The 4 Phases of Your Sleep Cycle
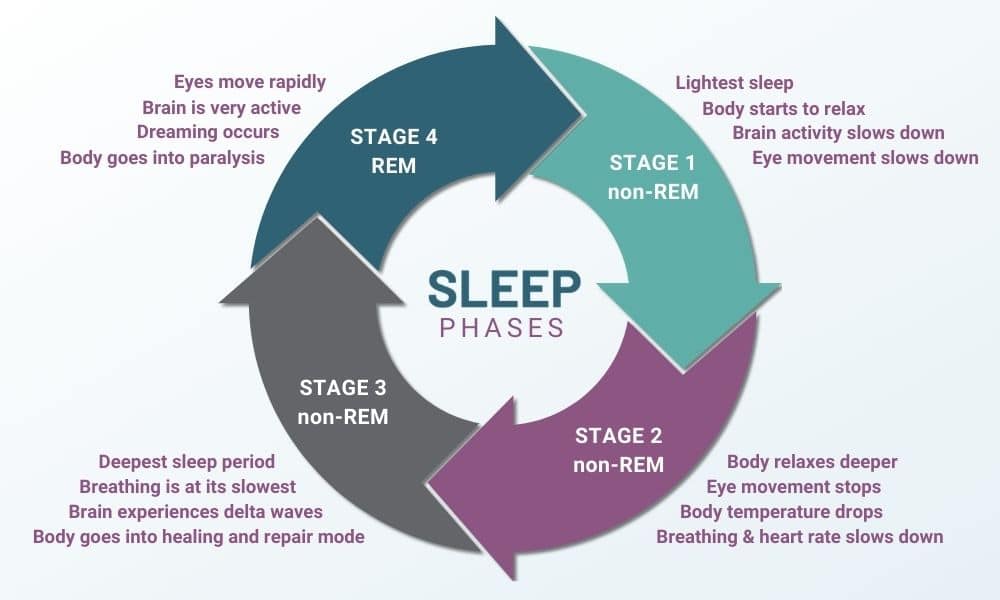
Stage 1 of non-REM Sleep / nR1
When you drift into sleep, you enter stage one of non-REM sleep; this period usually only lasts about 5 minutes. In this light sleeping period, you may still be aware of what is going on around you. Your body is not fully relaxed; however, your brain activity and eye movement begin to slow down, and you are now progressing into stage 2.
Stage 2 of non-REM Sleep / nR2
During Stage 2 of non-REM sleep, your body relaxes more, and you are no longer aware of what is going on around you. Your temperature will go down slightly, your breathing and heart rate slows, and your eye movement will stop. This period of sleep is about 10-25 minutes. Each time you enter the nR2 sleep stage, it gets longer throughout the night.
Stage 3 of non-REM Sleep / nR3
The last stage of non-REM sleep is a deep sleep period where breathing is at its slowest, brain activity is reduced, and your body is in a state of deep relaxation. The brain experiences patterns of delta waves during this time.
Tissue repair, regeneration of immune function, and healthy cell growth, along with other body and health benefits, occur during nR3. Your body releases hormones that support healing during this time.
During the first half of the night, we spend most of our time in this phase, about 20-40 minutes. As we continue cycling through the sleep phases, we spend less time in nR3 sleep and more time in REM sleep.
Stage 4 REM Sleep / REM
REM or rapid eye movement is the period of sleep where the brain activity increases and your body experiences atonia, where your muscles are temporarily paralyzed, except for the muscles that control your eyes and breathing. Your eyes are moving behind your eyelids, and your brain is very active; similar to when you are awake. At this time during your sleep cycle, you experience intense dreams. Light dreaming can occur in non-REM sleep phases; however, it is not very common.
It takes about 90 minutes to enter the first phase of REM sleep, and the first pass lasts only 10 minutes. As you cycle through the different sleep stages, each time you go into REM sleep, the duration will last longer. The later stages can last around an hour. For adults, 25% of total sleep time is spent in REM sleep.
This time in REM sleep supports your critical thinking, learning, cognitive function, creativity, and memory. REM sleep is crucial to your wellbeing and mental health.
There are a couple of things you can do to ensure you are getting enough REM sleep in each night for maximum wellness benefits and mental alertness.
Tips For Supporting REM Sleep:
- Don’t drink alcohol or caffeine at least 4 hours prior to sleep
- Get daily exercise
- Wind down for bed without screens and blue light
- Sleep in a quiet, dark, and cool room
- Stick to a sleep schedule and consistent bedtime
- Relax before bed to destress; read and enjoy a cup of tea
- Have one serving of Pure Sleep 30 minutes before bed to support deep sleep